Ultraviolet light is an electromagnetic wave of 100-380 nm in the intermediate wavelength range of X-ray and visible light. The UV-curing wavelength range is mostly 200-380 nm. In the use of the photoinitiator for the absorption wavelength and curing process requirements to select the appropriate light source, with the UV light meter, quantitative and accurate control of light intensity and exposure.
In the light source, high-pressure mercury lamps are more commonly used, and such light sources have higher light intensities at 254, 313, and 365 nm. Recent studies have found that doping metal halides such as SbI2, MnI2, and FeI2 in mercury lamps can enhance the radiation efficiency of UV-A (315-380 nm) light and develop a variety of new high-efficiency ultraviolet light sources.
The ultraviolet curing device has a variety of forms such as a fixed type, a portable type, and a spot-curing type according to the curing process requirements. In industry, special devices such as liquid crystal display (LCD) glass paste ultraviolet curing devices, liquid crystal injection hole sealing devices, and the like are often used.
2 Domestic and Foreign Status Quo
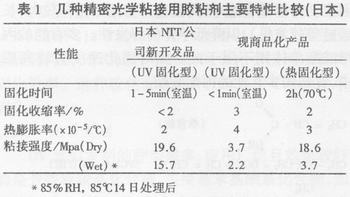
UV-curing adhesives are widely used in the bonding of optical devices such as optical fibers, optical lenses, etc. In recent years, there have also been numerous applications for the assembly of electronic devices for communication information. Chemence, Hoelne, Holdtite, Sartomer, Japan's East Asia Synthetic, Three Bond, and Heli Chemical Industry have developed many types of UV-curing adhesives. The shear strength can generally reach 8Mpa or more. Shrinkage is generally 2% -5%. As an example, several optical bonding adhesives produced and developed in Japan are listed in Table 1. In China, 53 of the Ordnance Industry Department, Chenguang Chemical Research Institute of the Ministry of Chemical Industry, and Yantai Debang Company also developed a small number of varieties, but there is a certain gap between the performance and the curing process compared with foreign countries. In recent years, domestic UV curing technology has developed rapidly, and the industry's annual growth rate is as high as 25%. The current patented UV-curable adhesives are mainly focused on photocurable oligomers, photoinitiators, and various components.
3 Development
The shortcomings of radical polymerization UV-curable adhesives are that the shrinkage rate is relatively large, mostly 2%-5%, far greater than the shrinkage of epoxy adhesives, and the second is lower heat resistance, at higher temperatures The dimensional stability is not good enough. In addition, acrylate-based materials are easily decomposed in water, and moisture resistance needs to be improved. Design and development of high-performance photosensitive resin or composite curing technology, such as UV + room temperature heat curing, UV + anaerobic curing, etc., to reduce the shrinkage of the adhesive, improve heat resistance, moisture resistance is the future direction of development.
(Author/Wu Jianwei, Yu Hong, Yu Yu, Fu Gang, He Yingcui, Fu Chunming Heilongjiang Research Institute of Petroleum Chemistry)
China Adhesive Information Industry Network